Connecting to Seawulf¶
We connect with secure shell or ssh from our terminal (GitBash or Putty on windows) to URI’s teaching High Performance Computing (HPC) Cluster Seawulf.
ssh -l brownsarahm seawulf.uri.edubrownsarahm@seawulf.uri.edu's password:
Permission denied, please try again.
brownsarahm@seawulf.uri.edu's password:
Permission denied, please try again.
brownsarahm@seawulf.uri.edu's password:
Last failed login: Tue Oct 28 12:34:16 EDT 2025 from 172.20.24.214 on ssh:notty
There were 4 failed login attempts since the last successful login.
Last login: Thu Oct 23 12:40:55 2025 from 172.20.24.214Today we actually want to start off the system, but make sure that you can log in to start.
logoutConnection to seawulf.uri.edu closed.Using ssh keys to authenticate¶
generate a key pair
store the public key on the server
Request to login, tell server your public key, get back a session ID from the server
if it has that public key, then it generates a random string, encrypts it with your public key and sends it back to your computer
On your computer, it decrypts the message + the session ID with your private key then hashes the message and sends it back
the server then hashes its copy of the message and session ID and if the hash received and calculated match, then you are loggied in
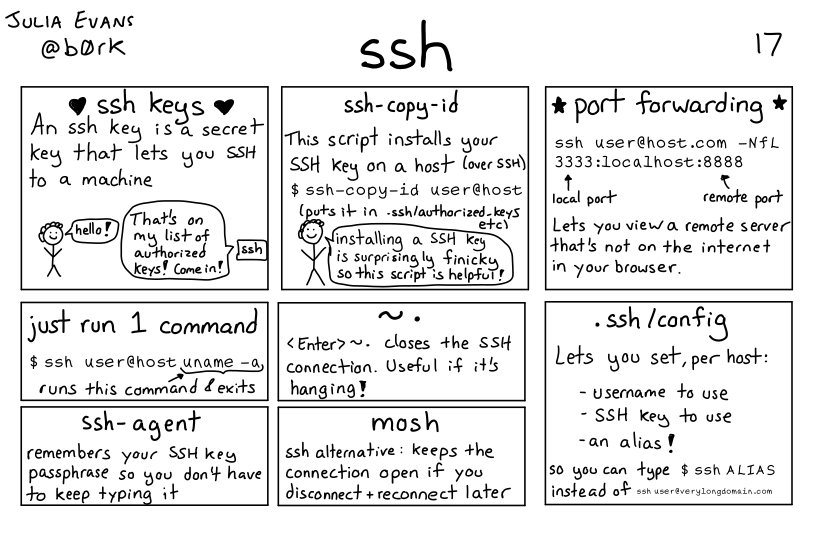
Lots more networking detals in the full zine available for purchase or I have a copy if you want to borrow it.
Generating a Key Pair¶
We can use ssh-keygen to create a keys.
-foption allows us to specify the file name of the keys.-toption allows us to specify the encryption algorithm-boption allows us to specify the size of the key in bits
ssh-keygen -f ~/seawulf -t rsa -b 1024Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter passphrase for "/Users/brownsarahm/seawulf" (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /Users/brownsarahm/seawulf
Your public key has been saved in /Users/brownsarahm/seawulf.pub
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:p6V3S6bkilzPf58lgoems+TB2Ekl2/KGkcMDrHQEe4Y brownsarahm@214.24.20.172.s.wireless.uri.edu
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 1024]----+
| ... |
| = |
| E * . . |
| . = o * |
| . S + |
| = & o |
| . @ O * . .|
| . =.@ * o..o|
| o =+=.o. o.|
+----[SHA256]-----+we can see the file that was created:
cdls -a. .lesshst Desktop
.. .local Documents
.bash_history .matplotlib Downloads
.bash_profile .npm Dropbox
.bash_sessions .ollama Library
.bashrc .python_history miniforge3
.cache .Rhistory Movies
.CFUserTextEncoding .ssh Music
.conda .Trash Pictures
.config .viminfo Public
.dropbox .vscode seawulf
.DS_Store .zprofile seawulf.pub
.gitconfig .zprofile.pysave Zotero
.ipython .zsh_history
.jupyter .zsh_sessionsSending the public key to a server¶
again -i to specify the file name
ssh-copy-id -i seawulf brownsarahm@seawulf.uri.edu/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "seawulf.pub"
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
brownsarahm@seawulf.uri.edu's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh -i ./seawulf 'brownsarahm@seawulf.uri.edu'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.To send it you have to type your password in, but it does not open a server connection.
Logging in¶
To login without using a password you have to tell ssh which key to use who to log in as and where to go:
ssh -i ./seawulf brownsarahm@seawulf.uri.eduLast login: Tue Oct 28 12:34:25 2025 from 172.20.24.214we’ll log out again and make it even less work!
logoutConnection to seawulf.uri.edu closed.First we’ll move the keys we made since we missed a step above
this puts them in a hidden ssh folder:
mv seawulf* .ssh/Now we’ll create (or add to) a ~/.ssh/config file
nano ~/.ssh/configand put this content in (but iwth your username, and a different pass for IdentityFile if needed)
Host seawulf
Hostname seawulf.uri.edu
user brownsarahm
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/seawulfnow we can log in with only:
ssh seawulfLast failed login: Tue Oct 28 12:56:44 EDT 2025 from 172.20.167.44 on ssh:notty
There were 3 failed login attempts since the last successful login.
Last login: Tue Oct 28 12:50:54 2025 from 172.20.24.214Using a compute node¶
salloc --helpUsage: salloc [OPTIONS(0)...] [ : [OPTIONS(N)]] [command(0) [args(0)...]]
Parallel run options:
-A, --account=name charge job to specified account
-b, --begin=time defer job until HH:MM MM/DD/YY
--bell ring the terminal bell when the job is allocated
--bb=<spec> burst buffer specifications
--bbf=<file_name> burst buffer specification file
-c, --cpus-per-task=ncpus number of cpus required per task
--comment=name arbitrary comment
--container Path to OCI container bundle
--cpu-freq=min[-max[:gov]] requested cpu frequency (and governor)
--delay-boot=mins delay boot for desired node features
-d, --dependency=type:jobid[:time] defer job until condition on jobid is satisfied
--deadline=time remove the job if no ending possible before
this deadline (start > (deadline - time[-min]))
-D, --chdir=path change working directory
--get-user-env used by Moab. See srun man page.
--gid=group_id group ID to run job as (user root only)
--gres=list required generic resources
--gres-flags=opts flags related to GRES management
-H, --hold submit job in held state
-I, --immediate[=secs] exit if resources not available in "secs"
-J, --job-name=jobname name of job
-k, --no-kill do not kill job on node failure
-K, --kill-command[=signal] signal to send terminating job
-L, --licenses=names required license, comma separated
-M, --clusters=names Comma separated list of clusters to issue
commands to. Default is current cluster.
Name of 'all' will submit to run on all clusters.
NOTE: SlurmDBD must up.
-m, --distribution=type distribution method for processes to nodes
(type = block|cyclic|arbitrary)
--mail-type=type notify on state change: BEGIN, END, FAIL or ALL
--mail-user=user who to send email notification for job state
changes
--mcs-label=mcs mcs label if mcs plugin mcs/group is used
-n, --ntasks=N number of processors required
--nice[=value] decrease scheduling priority by value
--no-bell do NOT ring the terminal bell
--ntasks-per-node=n number of tasks to invoke on each node
-N, --nodes=N number of nodes on which to run (N = min[-max])
-O, --overcommit overcommit resources
--power=flags power management options
--priority=value set the priority of the job to value
--profile=value enable acct_gather_profile for detailed data
value is all or none or any combination of
energy, lustre, network or task
-p, --partition=partition partition requested
-q, --qos=qos quality of service
-Q, --quiet quiet mode (suppress informational messages)
--reboot reboot compute nodes before starting job
-s, --oversubscribe oversubscribe resources with other jobs
--signal=[R:]num[@time] send signal when time limit within time seconds
--spread-job spread job across as many nodes as possible
--switches=max-switches{@max-time-to-wait}
Optimum switches and max time to wait for optimum
-S, --core-spec=cores count of reserved cores
--thread-spec=threads count of reserved threads
-t, --time=minutes time limit
--time-min=minutes minimum time limit (if distinct)
--uid=user_id user ID to run job as (user root only)
--use-min-nodes if a range of node counts is given, prefer the
smaller count
-v, --verbose verbose mode (multiple -v's increase verbosity)
--wckey=wckey wckey to run job under
Constraint options:
--cluster-constraint=list specify a list of cluster constraints
--contiguous demand a contiguous range of nodes
-C, --constraint=list specify a list of constraints
-F, --nodefile=filename request a specific list of hosts
--mem=MB minimum amount of real memory
--mincpus=n minimum number of logical processors (threads)
per node
--reservation=name allocate resources from named reservation
--tmp=MB minimum amount of temporary disk
-w, --nodelist=hosts... request a specific list of hosts
-x, --exclude=hosts... exclude a specific list of hosts
Consumable resources related options:
--exclusive[=user] allocate nodes in exclusive mode when
cpu consumable resource is enabled
--exclusive[=mcs] allocate nodes in exclusive mode when
cpu consumable resource is enabled
and mcs plugin is enabled
--mem-per-cpu=MB maximum amount of real memory per allocated
cpu required by the job.
--mem >= --mem-per-cpu if --mem is specified.
Affinity/Multi-core options: (when the task/affinity plugin is enabled)
For the following 4 options, you are
specifying the minimum resources available for
the node(s) allocated to the job.
--sockets-per-node=S number of sockets per node to allocate
--cores-per-socket=C number of cores per socket to allocate
--threads-per-core=T number of threads per core to allocate
-B --extra-node-info=S[:C[:T]] combine request of sockets per node,
cores per socket and threads per core.
Specify an asterisk (*) as a placeholder,
a minimum value, or a min-max range.
--ntasks-per-core=n number of tasks to invoke on each core
--ntasks-per-socket=n number of tasks to invoke on each socket
GPU scheduling options:
--cpus-per-gpu=n number of CPUs required per allocated GPU
-G, --gpus=n count of GPUs required for the job
--gpu-bind=... task to gpu binding options
--gpu-freq=... frequency and voltage of GPUs
--gpus-per-node=n number of GPUs required per allocated node
--gpus-per-socket=n number of GPUs required per allocated socket
--gpus-per-task=n number of GPUs required per spawned task
--mem-per-gpu=n real memory required per allocated GPU
Help options:
-h, --help show this help message
--usage display brief usage message
Other options:
-V, --version output version information and exitWe can get the default settings
sallocsalloc: Granted job allocation 28251
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration
salloc: Nodes n005 are ready for jobwe get a job
hostnameseawulf.uri.edupwd/home/brownsarahmlsbash-lesson.tar.gz SRR307025_2.fastq
dmel-all-r6.19.gtf SRR307026_1.fastq
dmel_unique_protein_isoforms_fb_2016_01.tsv SRR307026_2.fastq
gene_association.fb SRR307027_1.fastq
linecounts.txt SRR307027_2.fastq
seawulf SRR307028_1.fastq
seawulf.pub SRR307028_2.fastq
SRR307023_1.fastq SRR307029_1.fastq
SRR307023_2.fastq SRR307029_2.fastq
SRR307024_1.fastq SRR307030_1.fastq
SRR307024_2.fastq SRR307030_2.fastq
SRR307025_1.fastq timegrep --helpUsage: grep [OPTION]... PATTERN [FILE]...
Search for PATTERN in each FILE or standard input.
PATTERN is, by default, a basic regular expression (BRE).
Example: grep -i 'hello world' menu.h main.c
Regexp selection and interpretation:
-E, --extended-regexp PATTERN is an extended regular expression (ERE)
-F, --fixed-strings PATTERN is a set of newline-separated fixed strings
-G, --basic-regexp PATTERN is a basic regular expression (BRE)
-P, --perl-regexp PATTERN is a Perl regular expression
-e, --regexp=PATTERN use PATTERN for matching
-f, --file=FILE obtain PATTERN from FILE
-i, --ignore-case ignore case distinctions
-w, --word-regexp force PATTERN to match only whole words
-x, --line-regexp force PATTERN to match only whole lines
-z, --null-data a data line ends in 0 byte, not newline
Miscellaneous:
-s, --no-messages suppress error messages
-v, --invert-match select non-matching lines
-V, --version display version information and exit
--help display this help text and exit
Output control:
-m, --max-count=NUM stop after NUM matches
-b, --byte-offset print the byte offset with output lines
-n, --line-number print line number with output lines
--line-buffered flush output on every line
-H, --with-filename print the file name for each match
-h, --no-filename suppress the file name prefix on output
--label=LABEL use LABEL as the standard input file name prefix
-o, --only-matching show only the part of a line matching PATTERN
-q, --quiet, --silent suppress all normal output
--binary-files=TYPE assume that binary files are TYPE;
TYPE is 'binary', 'text', or 'without-match'
-a, --text equivalent to --binary-files=text
-I equivalent to --binary-files=without-match
-d, --directories=ACTION how to handle directories;
ACTION is 'read', 'recurse', or 'skip'
-D, --devices=ACTION how to handle devices, FIFOs and sockets;
ACTION is 'read' or 'skip'
-r, --recursive like --directories=recurse
-R, --dereference-recursive
likewise, but follow all symlinks
--include=FILE_PATTERN
search only files that match FILE_PATTERN
--exclude=FILE_PATTERN
skip files and directories matching FILE_PATTERN
--exclude-from=FILE skip files matching any file pattern from FILE
--exclude-dir=PATTERN directories that match PATTERN will be skipped.
-L, --files-without-match print only names of FILEs containing no match
-l, --files-with-matches print only names of FILEs containing matches
-c, --count print only a count of matching lines per FILE
-T, --initial-tab make tabs line up (if needed)
-Z, --null print 0 byte after FILE name
Context control:
-B, --before-context=NUM print NUM lines of leading context
-A, --after-context=NUM print NUM lines of trailing context
-C, --context=NUM print NUM lines of output context
-NUM same as --context=NUM
--group-separator=SEP use SEP as a group separator
--no-group-separator use empty string as a group separator
--color[=WHEN],
--colour[=WHEN] use markers to highlight the matching strings;
WHEN is 'always', 'never', or 'auto'
-U, --binary do not strip CR characters at EOL (MSDOS/Windows)
-u, --unix-byte-offsets report offsets as if CRs were not there
(MSDOS/Windows)
'egrep' means 'grep -E'. 'fgrep' means 'grep -F'.
Direct invocation as either 'egrep' or 'fgrep' is deprecated.
When FILE is -, read standard input. With no FILE, read . if a command-line
-r is given, - otherwise. If fewer than two FILEs are given, assume -h.
Exit status is 0 if any line is selected, 1 otherwise;
if any error occurs and -q is not given, the exit status is 2.
Report bugs to: bug-grep@gnu.org
GNU Grep home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/grep/>
General help using GNU software: <http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>grep mRNA dmel-all-r6.19.gtfX FlyBase mRNA 19961689 19968479 . + . gene_id "FBgn0031081"; gene_symbol "Nep3"; transcript_id "FBtr0070000"; transcript_symbol "Nep3-RA";
2L FlyBase mRNA 781276 782885 . + . gene_id "FBgn0041250"; gene_symbol "Gr21a"; transcript_id "FBtr0331651"; transcript_symbol "Gr21a-RB";We can also count the occurences
grep -c mRNA dmel-all-r6.19.gtf34025wc -l dmel-all-r6.19.gtf542048 dmel-all-r6.19.gtfScripts and Permissions¶
we will set a very simple script
nano demo.shecho "script works"If we want to run the file, we can use bash directly,
bash demo.shscript worksthis is limited relative to calling our script in other ways.
One thing we could do is to run the script using ./
./demo.shbash: ./demo.sh: Permission deniedBy default, files have different types of permissions: read, write, and execute for different users that can access them. To view the permissions, we can use the -l option of ls.
ls -lhtotal 136M
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 12M Apr 18 2021 bash-lesson.tar.gz
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 21 Oct 28 13:12 demo.sh
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 74M Jan 16 2018 dmel-all-r6.19.gtf
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 705K Jan 25 2016 dmel_unique_protein_isoforms_fb_2016_01.tsv
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 24M Jan 25 2016 gene_association.fb
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 432 Oct 23 13:34 linecounts.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307023_1.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307023_2.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307024_1.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307024_2.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307025_1.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307025_2.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307026_1.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307026_2.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307027_1.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307027_2.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307028_1.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307028_2.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307029_1.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307029_2.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307030_1.fastq
-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 1.6M Jan 25 2016 SRR307030_2.fastq
drwxr-xr-x. 2 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 97 Dec 3 2024 timeFor each file we get 10 characters in the first column that describe the permissions. The 3rd column is the username of the owner, the fourth is the group, then size date revised and the file name.
We are most interested in the 10 character permissions. The fist column indicates if any are directories with a d or a - for files. We have no directories, but we can create one to see this.
We can see in the bold line, that the first character is a d.
The next nine characters indicate permission to Read, Write, and eXecute a file. With either the letter or a - for permissions not granted, they appear in three groups of three, three characters each for owner, group, anyone with access.
we can use grep to make the output shorter:
ls -l | grep demo.sh-rw-r--r--. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 21 Oct 28 13:12 demo.shTo add execute permission, we can use chmod with +x
chmod +x demo.shand confirm it worked:
ls -l | grep demo.sh-rwxr-xr-x. 1 brownsarahm spring2022-csc392 21 Oct 28 13:12 demo.shand can run the file
./demo.shscript worksNow we will set the script up to create a file that has th first 5 lines of eachh .fastq file
nano demo.shecho "script works"
for file in $(ls *.fastq)
do
echo $file >> fastq_head.txt
head -n 5 $file >> fastq_head.txt
doneand then give up the interactive session
exitexit
salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 28251
salloc: Job allocation 28251 has been revoked.we can still run this simple script on the login node, but that is not best practice
./demo.shscript workswe can check the result to make sure it looks right
head -n 3 fastq_head.txtSRR307023_1.fastq
@SRR307023.37289418.1 GA-C_0019:1:120:7087:20418 length=101
CGAGCGACTTTTGTATAACTATATTTTTCTCGTTCTTGGCTCCGACATCTATACAAATTCAGAAGGCAGTTTTGCGCGTGGAGGGACAATTACAAATTGAGNow, we wil make a batch job
nano my_job.sh#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 1:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
./demo.shthere are a lot of sbatch options
and submit it:
sbatch my_job.shSubmitted batch job 28259lsbash-lesson.tar.gz SRR307023_1.fastq SRR307027_2.fastq
demo.sh SRR307023_2.fastq SRR307028_1.fastq
dmel-all-r6.19.gtf SRR307024_1.fastq SRR307028_2.fastq
dmel_unique_protein_isoforms_fb_2016_01.tsv SRR307024_2.fastq SRR307029_1.fastq
fastq_head.txt SRR307025_1.fastq SRR307029_2.fastq
gene_association.fb SRR307025_2.fastq SRR307030_1.fastq
linecounts.txt SRR307026_1.fastq SRR307030_2.fastq
my_job.sh SRR307026_2.fastq time
slurm-28259.out SRR307027_1.fastqThe out file contains the stdout and stderr streams from when your script ran.
cat slurm-28259.outscript worksWe can also remove with -x
chmod -x demo.sh./demo.sh-bash: ./demo.sh: Permission deniedsbatch my_job.shSubmitted batch job 28269ls | grep .outslurm-28259.out
slurm-28269.outcat slurm-28269.out/var/spool/slurmd/job28269/slurm_script: line 4: ./demo.sh: Permission deniedsbatch --helpUsage: sbatch [OPTIONS(0)...] [ : [OPTIONS(N)...]] script(0) [args(0)...]
Parallel run options:
-a, --array=indexes job array index values
-A, --account=name charge job to specified account
--bb=<spec> burst buffer specifications
--bbf=<file_name> burst buffer specification file
-b, --begin=time defer job until HH:MM MM/DD/YY
--comment=name arbitrary comment
--cpu-freq=min[-max[:gov]] requested cpu frequency (and governor)
-c, --cpus-per-task=ncpus number of cpus required per task
-d, --dependency=type:jobid[:time] defer job until condition on jobid is satisfied
--deadline=time remove the job if no ending possible before
this deadline (start > (deadline - time[-min]))
--delay-boot=mins delay boot for desired node features
-D, --chdir=directory set working directory for batch script
-e, --error=err file for batch script's standard error
--export[=names] specify environment variables to export
--export-file=file|fd specify environment variables file or file
descriptor to export
--get-user-env load environment from local cluster
--gid=group_id group ID to run job as (user root only)
--gres=list required generic resources
--gres-flags=opts flags related to GRES management
-H, --hold submit job in held state
--ignore-pbs Ignore #PBS and #BSUB options in the batch script
-i, --input=in file for batch script's standard input
-J, --job-name=jobname name of job
-k, --no-kill do not kill job on node failure
-L, --licenses=names required license, comma separated
-M, --clusters=names Comma separated list of clusters to issue
commands to. Default is current cluster.
Name of 'all' will submit to run on all clusters.
NOTE: SlurmDBD must up.
--container Path to OCI container bundle
-m, --distribution=type distribution method for processes to nodes
(type = block|cyclic|arbitrary)
--mail-type=type notify on state change: BEGIN, END, FAIL or ALL
--mail-user=user who to send email notification for job state
changes
--mcs-label=mcs mcs label if mcs plugin mcs/group is used
-n, --ntasks=ntasks number of tasks to run
--nice[=value] decrease scheduling priority by value
--no-requeue if set, do not permit the job to be requeued
--ntasks-per-node=n number of tasks to invoke on each node
-N, --nodes=N number of nodes on which to run (N = min[-max])
-o, --output=out file for batch script's standard output
-O, --overcommit overcommit resources
-p, --partition=partition partition requested
--parsable outputs only the jobid and cluster name (if present),
separated by semicolon, only on successful submission.
--power=flags power management options
--priority=value set the priority of the job to value
--profile=value enable acct_gather_profile for detailed data
value is all or none or any combination of
energy, lustre, network or task
--propagate[=rlimits] propagate all [or specific list of] rlimits
-q, --qos=qos quality of service
-Q, --quiet quiet mode (suppress informational messages)
--reboot reboot compute nodes before starting job
--requeue if set, permit the job to be requeued
-s, --oversubscribe over subscribe resources with other jobs
-S, --core-spec=cores count of reserved cores
--signal=[[R][B]:]num[@time] send signal when time limit within time seconds
--spread-job spread job across as many nodes as possible
--switches=max-switches{@max-time-to-wait}
Optimum switches and max time to wait for optimum
--thread-spec=threads count of reserved threads
-t, --time=minutes time limit
--time-min=minutes minimum time limit (if distinct)
--uid=user_id user ID to run job as (user root only)
--use-min-nodes if a range of node counts is given, prefer the
smaller count
-v, --verbose verbose mode (multiple -v's increase verbosity)
-W, --wait wait for completion of submitted job
--wckey=wckey wckey to run job under
--wrap[=command string] wrap command string in a sh script and submit
Constraint options:
--cluster-constraint=[!]list specify a list of cluster constraints
--contiguous demand a contiguous range of nodes
-C, --constraint=list specify a list of constraints
-F, --nodefile=filename request a specific list of hosts
--mem=MB minimum amount of real memory
--mincpus=n minimum number of logical processors (threads)
per node
--reservation=name allocate resources from named reservation
--tmp=MB minimum amount of temporary disk
-w, --nodelist=hosts... request a specific list of hosts
-x, --exclude=hosts... exclude a specific list of hosts
Consumable resources related options:
--exclusive[=user] allocate nodes in exclusive mode when
cpu consumable resource is enabled
--exclusive[=mcs] allocate nodes in exclusive mode when
cpu consumable resource is enabled
and mcs plugin is enabled
--mem-per-cpu=MB maximum amount of real memory per allocated
cpu required by the job.
--mem >= --mem-per-cpu if --mem is specified.
Affinity/Multi-core options: (when the task/affinity plugin is enabled)
For the following 4 options, you are
specifying the minimum resources available for
the node(s) allocated to the job.
--sockets-per-node=S number of sockets per node to allocate
--cores-per-socket=C number of cores per socket to allocate
--threads-per-core=T number of threads per core to allocate
-B --extra-node-info=S[:C[:T]] combine request of sockets per node,
cores per socket and threads per core.
Specify an asterisk (*) as a placeholder,
a minimum value, or a min-max range.
--ntasks-per-core=n number of tasks to invoke on each core
--ntasks-per-socket=n number of tasks to invoke on each socket
GPU scheduling options:
--cpus-per-gpu=n number of CPUs required per allocated GPU
-G, --gpus=n count of GPUs required for the job
--gpu-bind=... task to gpu binding options
--gpu-freq=... frequency and voltage of GPUs
--gpus-per-node=n number of GPUs required per allocated node
--gpus-per-socket=n number of GPUs required per allocated socket
--gpus-per-task=n number of GPUs required per spawned task
--mem-per-gpu=n real memory required per allocated GPU
Help options:
-h, --help show this help message
--usage display brief usage message
Other options:
-V, --version output version information and exitsbatch --help | grep output -o, --output=out file for batch script's standard output
--parsable outputs only the jobid and cluster name (if present),
-V, --version output version information and exitsbatch --help | grep job -a, --array=indexes job array index values
-A, --account=name charge job to specified account
-b, --begin=time defer job until HH:MM MM/DD/YY
-d, --dependency=type:jobid[:time] defer job until condition on jobid is satisfied
--deadline=time remove the job if no ending possible before
--gid=group_id group ID to run job as (user root only)
-H, --hold submit job in held state
-J, --job-name=jobname name of job
-k, --no-kill do not kill job on node failure
--mail-user=user who to send email notification for job state
--no-requeue if set, do not permit the job to be requeued
--parsable outputs only the jobid and cluster name (if present),
--priority=value set the priority of the job to value
--reboot reboot compute nodes before starting job
--requeue if set, permit the job to be requeued
-s, --oversubscribe over subscribe resources with other jobs
--spread-job spread job across as many nodes as possible
--uid=user_id user ID to run job as (user root only)
-W, --wait wait for completion of submitted job
--wckey=wckey wckey to run job under
cpu required by the job.
the node(s) allocated to the job.
-G, --gpus=n count of GPUs required for the jobnano demo.shchmod +x demo.shsqueue --me JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)sbatch my_job.shSubmitted batch job 28276squeue --me JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
28276 general my_job.s brownsar R 0:02 1 n005squeue --me JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
28276 general my_job.s brownsar R 0:53 1 n005sbatch my_job.shSubmitted batch job 28282ls | grep .outslurm-28259.out
slurm-28269.out
slurm-28276.out
slurm-28282.outnano my_job.shcat my_job.sh#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 1:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH -o smb%j.out
./demo.shsbatch my_job.shSubmitted batch job 28286squeue --me JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
28286 general my_job.s brownsar R 0:08 1 n005ls | grep .outslurm-28259.out
slurm-28269.out
slurm-28276.out
slurm-28282.out
smb28286.outsqueue --me JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
28286 general my_job.s brownsar R 0:27 1 n005logoutConnection to seawulf.uri.edu closed.Helping add explanation to this is eligible for a community badge
Prepare for Next Class¶
Think about what you know about code compilation, be ready to discuss.
Refresh your memory of where in this course we have talked about building content
ensure you can log into seawulf
Badges¶
Review the notes from today
Read through this rsa encryption demo site to review how it works. Find 2 other encyrption algorithms that could be used with ssh (hint: try
man sshor read it online) and compare them in encyryption_compare. Your comparison should be enough to advise someone which is best and why, but need not get into the details.File permissions are represented numerically often in octal, by transforming the permissions for each level (owner, group, all) as binary into a number. Add octal.md to your KWL repo and answer the following. Try to think through it on your own, but you may look up the answers, as long as you link to (or ideally cite using jupyterbook citations) a high quality source.
1. Describe how to transform the permissions [`r--`, `rw-`, `rwx`] to octal, by treating each set as three bits. 1. Transform the permission we changed our script to `rwxr-xr-x` to octal. 1. Which of the following would prevent a file from being edited by other people 777 or 755 and why?
Review the notes from today
configure ssh keys for your github account
Find 2 other encyrption algorithms that could be used wiht ssh (hint: try
man sshor read it online) and compare them in encyryption_compare. Your comparison should be enough to advise someone which is best and why, but need not get into the details.Read through this rsa encryption demo site site and use it to show what, for a particular public/private key pair (based on small primes) it would look like to pass a message, “It is spring now!” encrypted. (that is encypt it, and decrypt it with the site, show it’s encrypted version and the key pair and describe what would go where). Put your example in rsademo.md.
Experience Report Evidence¶
In office hours, show your files on seawulf.
Questions After Today’s Class¶
Can I remove a passphrase after adding one for a key?¶
You can change it with:
ssh-keygen -pand if you set the new one to blank, it’s removed
How can multiple SLURM jobs communicate with each other?¶
I think this is not soemthing they can do, in general, but through written files they could.
Typical use, however, is that you split workinto multiple jobs in chunks that do not need to share data.
What are the most common use cases for grep?¶
Finding things in long files.